Course Content
-
Pediatric Heart Failure: “How to approach the management of Pediatric Heart Failure” Understanding heart failure: the basics in pediatric heart failure and congenital heart diseases. Basics of treatment and decision making in clinic cases
- Introduction. Definition of Heart Failure
- Etiology of Heart Failure in pediatric age
- Pathophysiology of Heart Failure
- Heart Failure in Congenital Heart Disease
- Natriuretic peptid system
- Biomarkers in Heart Failure
- Signs and Symptoms in pediatric age
- Classification of severity in pediatric Heart Failure
- Different forms of cardiomyopathies: “Diagnostic techniques and treatments”
- Dilated Cardiomyopathy
- Myocarditis
- Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy
- Restrictive Cardiomyopathy
- Non-compaction Cardiomyopathy
- Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Dysplasia (ARVD)
- Evaluation Cardiomyopathies and Genetics
- Evaluation Quiz
- Arrhythmias in Pediatric Heart Failure: EKG abnormalities
- Indications ICD in adults and pediatric age
- Clinic Cases. Quiz
- Treatment in chronic pediatric Heart Failure
- New treatment: Sacubitril – Valsartan
- New therapies and Experimental
- Summary Pediatric Heart Failure therapies
-
Basic and Advanced Echocardiography in Pediatric Heart Failure Description of basic and advanced echocardiography tools for diagnostic and follow-up of children affected by heart failure
- Journal Club: “Basic and advanced echocardiography in advanced heart failure: an overview”
- LV systolic function
- RV systolic function
- Cardiac Diastolic Function and Diastolic Heart Failure
- Tissue Doppler Imaging (DTI) and diastolic dysfunction
- Summary Echo left diastolic dysfunction
- RV diastolic dysfunction
- Management of pediatric diastolic dysfunction
- Clinic Cases
- dP/dt LV function assessment
- Myocardial Performance Index (Tei Index) Doppler Mitral Flow
- Myocardial Performance Index (Tei Index) DTI
- Basics of Strain and Strain-rate
- Global longitudinal Strain (GLS)
- Cardiac output assessment by Echo
- Advanced Imaging in Pediatric Heart Failure
- Echocardiography: Apps and webs
- Clinic Cases
-
Pediatric Heart Transplant (I) Basic in inmunology and rejection. Indications of pediatric heart transplant and contraindications. Mechanical support in pediatric age. Surgery and perioperative treatment.
- Basis of transplant immunology
- Human leucocytes antigen (HLA)
- Blood group antigen (ABO)
- Graft Rejection
- Donor selection & evaluation
- Tissue typing and cross matching
- Ischemic time and the TransMedics® Organ Care System (OCS™)
- Indications and Contraindications of Pediatric Heart Transplant
- Indications of pediatric Mechanical cardiac support (MCS)
- Types of Devices for pediatric MCS
- VAD selection for pediatric MCS
- Surgery of Heart Transplant in pediatric age and in Congenital heart disease
- Principle Challenge in immunosuppressive therapies
- Induction therapy during surgery, postoperative period and denervated heart
-
Pediatric Heart Transplant (II) Basic of immunosuppression treatment. Management of rejection and infections in pediatric heart transplant. Information for patients and relatives. Outcomes of heart transplant and indications of retransplantation
- Basis of immunosuppression therapy
- Risk of infection after transplantation
- Complication of chronic immunosuppression
- Basis of Rejection and assessment
- Endomyocardial biopsy and rejection
- Treatment of humoral and cellular rejection
- Chronic rejection: Coronary Artery Vasculopathy (CAV)
- Clinic follow-up in patient transplanted
- Cardiac Rehabilitation in pediatric heart transplant
- Survival and Causes of death in pediatric heart transplant
- Indications of retransplantation and survival
- Home Care after Pediatric Heart Transplant
- Palliative care in Pediatric Heart Failure and Heart Transplantation
- Future perspectives. Summary
- Clinic cases
-
Final Quizz Congratulations! You finished the course, check your knowledge with this final test
-
Fellow Evaluation Course Evaluation of the cardiac fellows who attended the course in May 2020
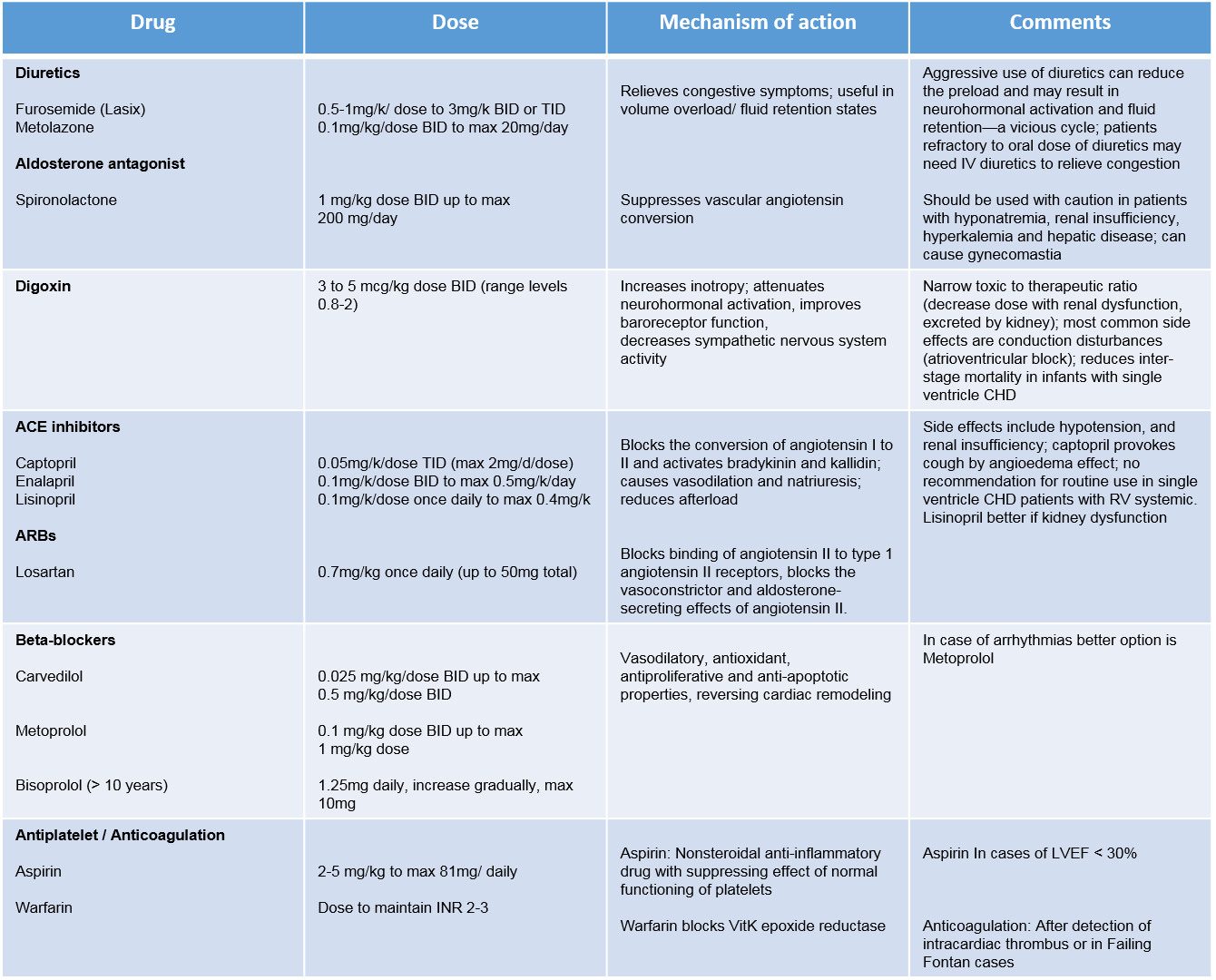
Treatment in chronic pediatric Heart Failure
Current management of acute HF are focus in improvement of hemodynamics and prevent deterioration and includes stabilization with intravenous inotropes/vasopressors, mechanical ventilation, treatment of arrhythmia, and progression to mechanical support, if needed. The goal in chronic HF is prevent progression, and provide a reasonable clinical status of the children to allow somatic growth and optimal development. Treatment in HF is based in avoiding the mechanisms neurohormonals.
Drug trials in pediatric cardiomyopathy are challenging because of limitations in power because of small sample size, lack of validated end points, and incomplete pharmacokinetic /pharmacodynamic data. Despite the lack of sufficient randomized prospective studies, angiotensin-converting enzyme antagonists inhibitors (ACEi) are the first-line therapy and beta-blockers are second-line in children. Beta-blockers have to start when patient has been stabilized, never in acute HF episode, carvedilol is the first choice, starting with a low dose and titrating every 2 weeks to check tolerance, in case of arrhythmias, metoprolol is better option. Mineralocorticoids are accepted at the beginning of the episodes while diuretics should be used to achieve a euvolemic status.
Digoxin has been studied extensively in adults with congestive HF, in whom there is some evidence of acute hemodynamic benefit in chronic congestive, decreasing the rate of hospitalization and improved quality of life, but not survival. Despite the lack of data regarding its use in children, digoxin continues to be used by most clinicians in the management of pediatric heart failure due to low cost, and continued confidence in the usefulness of the drug based on long years of experience.
The common drugs used in pediatric HF (except anti-arrhythmics treatment) and mechanism of actions are summarized in this Table: